Non-polluting construction materials
Composites are revolutionizing the construction sector to make it more sustainable and resilient
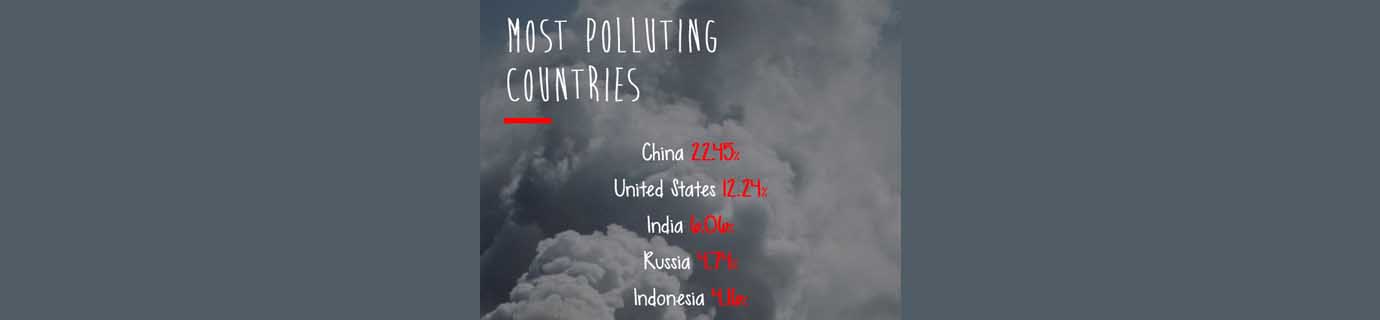
The construction sector has traditionally been one of the most important industries, as well as one of the most polluting. The data says it all:
- Globally it consumes 50% of all natural resources and 40% of energy, and generates 50% of all waste
- It requires over 2 tons of raw material for each square meter of housing built
- The energy used to make materials to build a house is equivalent to a third of the energy consumption of the average home during 50 years
- The waste generated by construction and demolition is over one ton per inhabitant per year.
The usual construction materials, such as steel, concrete, asbestos, certain kinds of paint and varnishes, elements of radon gas, uranium, lead and mercury, contaminate the environment and can cause illness, mainly due to the high consumption of energy and raw materials associated with their mining and extraction, production, treatment, transport and installation processes.
Fortunately, research and development has achieved significant progress in construction and today it is possible to build sustainable infrastructure, which is also resilient, largely due to the use of composite materials.
What are composite materials?
Composite materials are the combination of two or more materials so that the properties of the final material are superior to those of the two components separately. This kind of material, used initially by the aerospace industry, are increasingly used in the construction sector, both in civil engineering works and buildings.

The substitution of composite for traditional materials is an important change in favor of sustainability, since the former use mainly carbon or glass fibers bonded with polymers through processes such as hand lay-up, pultrusion, RTM (resin transfer molding) and high thickness infusion. These innovative processes consume less energy and produce materials offering superior performance to the traditional ones.
Benefits of composite materials
The use of composite materials, instead of elements such as concrete and steel, has many advantages:
- Lightness: the density of the materials varies from 0.03 to 2 kg/dm3, which enables assembly, transport and on-site placement
- Corrosion: the materials perform excellently against corrosion and environmental agents, which sees them often employed in coastal zones and reduces maintenance costs
- High mechanical resistance: this means they can support more weight, justifying their use as structural materials
- Malleable: they are very free in their capacity for molding, lending their design to any form
- Self-cleaning: they are not affected by rain, since they repel water, allowing their use in outside structural elements such as roofs, façades and ornamental features
- Tailor-made finishes: they enable different types of surface finish, offering different grades of luminosity
- They offer diverse acoustic and thermal insulation properties
- They can be easily repaired and reinforced.
Given all these benefits and the lesser pollution effect, the use of composite materials is revolutionizing the construction industry, making it more sustainable.
Future challenges
With a view to continuous improvement, researchers still need to overcome several challenges to adapt composite materials to more applications. Despite the benefits mentioned above, there are still some aspects that can be bettered, such as recyclability and fire resistance. Innovation departments in various companies in the sector are already working on these challenges.
Sources: ACCIONA, Detea, Aimplas and Construmática.