Do you know what the greenhouse effect is? It is the natural phenomenon that allows our planet to maintain the necessary conditions to harbor life. The atmosphere captures some of the sun's rays that reach the earth's crust, keeping them inside to get an average temperature of 15 0C. If the atmosphere did not catch any of these rays that bounce off the surface, the average temperature of the Earth would be -18 0C.
The atmosphere is composed of various natural gases, of which nitrogen, oxygen and argon constitute the 99.93%. However, there are other gases such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and ozone which have a greater impact on the greenhouse effect. Moreover, artificial gases called chlorofluorocarbons are also present in the atmosphere.
Consequences of the greenhouse effect
In the right proportion, these gases perform their duty, but when its concentration increases by the action of man, the atmosphere retains more heat than necessary, causing the rising of temperatures, melting ice caps, desertification, fires, storms and floods.
Why do greenhouse gases increase? There are three main reasons: the burning of fossil fuels like oil, coal and natural gas, forest deforestation and destruction of marine ecosystems that absorb carbon dioxide and the increase of a population that increasingly consumes natural resources.
To understand what the greenhouse effect is, why it is caused and the consequences for the planet we present this explanatory video that will solve many of your questions.
NASA documents the greenhouse effect
NASA satellites show how the greenhouse effect boosted by human action contributes to global warming:

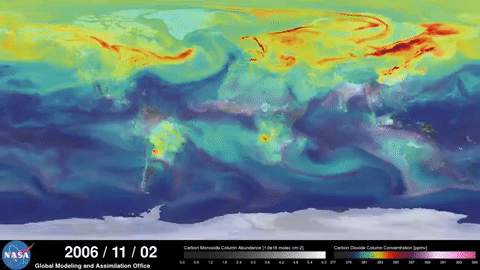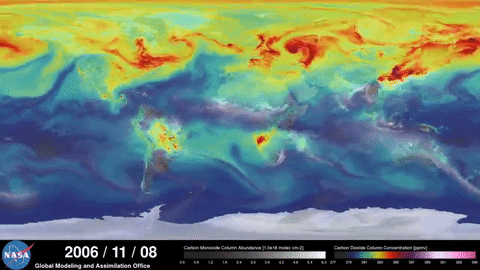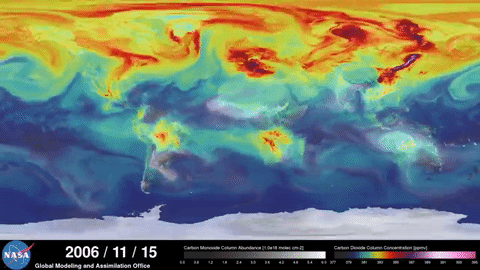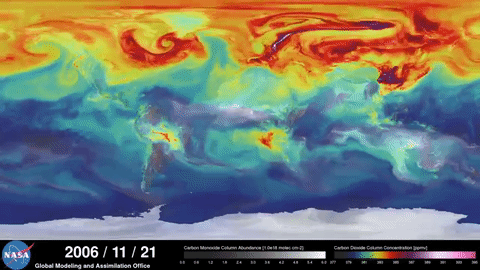
NASA Video 1 and NASA Video 2.
Incidence of the human being in the greenhouse effect
Human activity increases the concentration of greenhouse gases (GHG) in the atmosphere maximizing global warming.
By activity sectors, anthropogenic GHG emissions sources are:
- Electricity and heat production: 25%
- Agriculture and other land uses: 24%
- Transportation: 14%
- Industry: 21%
- Other energy: 10%
- Buildings: 6%
To curb the concentration of GHG in the atmosphere, it is necessary to focus on renewable energy sources that allow emissions reductions and preserve the oceans and forests, which represent the planet's natural carbon sinks and absorb part of the carbon dioxide.
In this infographic we compile the causes and consequences of the greenhouse effect, as well as the anthropogenic origin of emissions that threaten the life of the species.
